byte to megabit – How to convert B to Mbit
You’ll often see megabits and bytes floating around when dealing with internet speeds, downloads, and storage — but they’re not the same. A byte measures stored data, while a megabit is more common in data transmission. So, if your internet speed is listed in megabits and your file size is in bytes, converting between them can clear up the confusion.
Here’s how to convert bytes to megabits, along with what each unit really means.
What is a byte (B)?
A byte is a unit of digital information made up of 8 bits. It’s the standard unit for storage and file size in computing. Whether you’re downloading a PDF, saving an image, or copying a document, bytes (and their multiples like kilobytes or gigabytes) are the common currency.
Examples of byte use include:
-
File sizes (e.g., 2 MB PDF = 2 million bytes)
-
RAM and storage capacity
-
Text and binary data formats
What is a megabit (Mbit)?
A megabit is a unit of digital data equal to 1,000,000 bits (under the decimal system). It’s often abbreviated as Mbit or sometimes Mb (not to be confused with megabyte, MB).
Megabits are frequently used in:
-
Internet speed ratings (e.g., 100 Mbps = 100 megabits per second)
-
Network bandwidth
-
Streaming bitrate calculations
Since 1 byte = 8 bits, and 1 megabit = 1,000,000 bits, we can easily create a conversion path.
How to convert byte to megabit
We start with:
1 byte = 8 bits
1 megabit = 1,000,000 bits
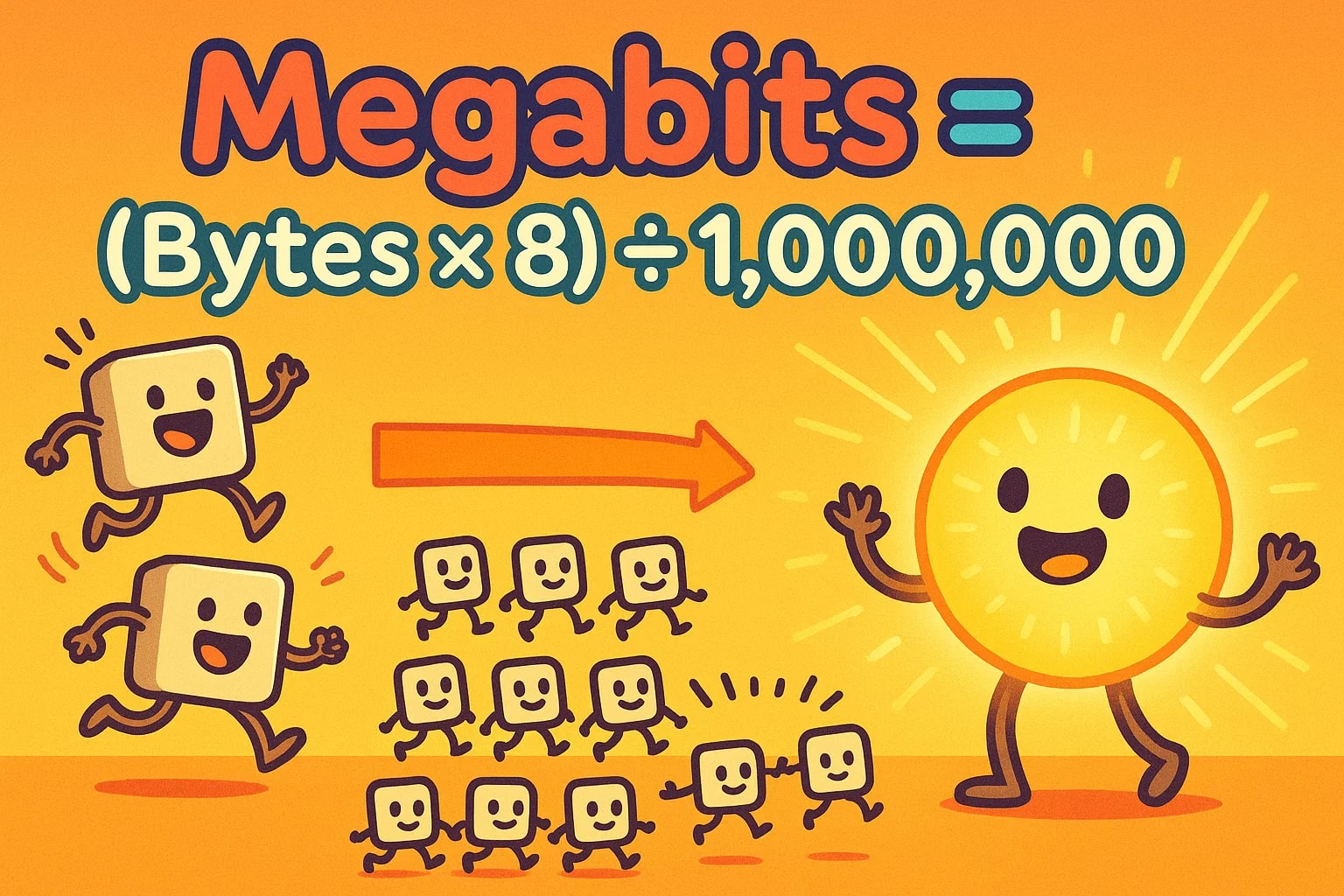
So, the formula becomes:
megabits = (bytes × 8) ÷ 1,000,000
✅ Example: Convert 1,250,000 bytes to megabits
megabits = (1,250,000 × 8) ÷ 1,000,000
megabits = 10
So, 1,250,000 bytes equals 10 megabits.
For quicker calculations, head to our Data Storage Converter or check out more conversion options via our Conversion tools.
Did you know?
-
Internet providers use megabits per second (Mbps) to describe download/upload speeds, while file sizes on your device are in megabytes (MB).
-
To download a 10 MB file on a 40 Mbps connection takes about 2 seconds — because 10 MB = 80 Mbit.
-
Streaming services like Netflix recommend speeds in Mbps — HD quality needs about 5 Mbps, which is 0.625 MB/s.
-
In network engineering, converting between bytes and megabits is essential for calculating throughput, latency, and load balancing.
-
Many modems and routers log traffic in bytes, while ISPs advertise in megabits — converting between them helps you compare apples to apples.
From storage to speed – Where bytes meet megabits
When the early web took off in the 1990s, dial-up internet ran at speeds of 56 Kbps — kilobits per second. That’s just 7 KB/s, barely fast enough to load a modern image file. Back then, bytes were how users thought about their storage, while megabits were the language of networks and bandwidth.
As speeds improved and media grew heavier, bridging the gap between storage units (like bytes) and transfer units (like megabits) became critical. Today, whether you’re planning a server upgrade or calculating how long it’ll take to download a game, converting byte to megabit is still a common need.
From files to fiber – the conversion that keeps things moving
So, here’s your formula again:
megabits = (bytes × 8) ÷ 1,000,000
It’s a fast, simple way to translate between data size and data flow — a key connection for anyone dealing with files, networks, or digital systems.
Want to explore more conversions? Use our Data Storage Converter or browse all Conversion tools to stay precise across every unit.

