centimeter to nanometer – How to convert cm to nm
Switching from centimeter to nanometer lets us step from a visible unit into one that operates at the atomic and molecular scale. The centimeter is used in schools, design, and everyday life, while the nanometer is crucial for nanotechnology, biology, and physics. Learning how to convert cm to nm provides a simple but powerful link between the two.
What is a Centimeter (cm)?
A centimeter is a metric unit equal to one hundredth of a meter. It equals 10 millimeters or 0.01 meter. It is common in daily measurements like paper size, furniture, and body height.
What is a Nanometer (nm)?
A nanometer is one billionth of a meter:1 nm = 10⁻⁹ m.
It is used to describe the size of atoms, molecules, wavelengths of light, and semiconductor features. For example, a strand of DNA is about 2 nm wide.
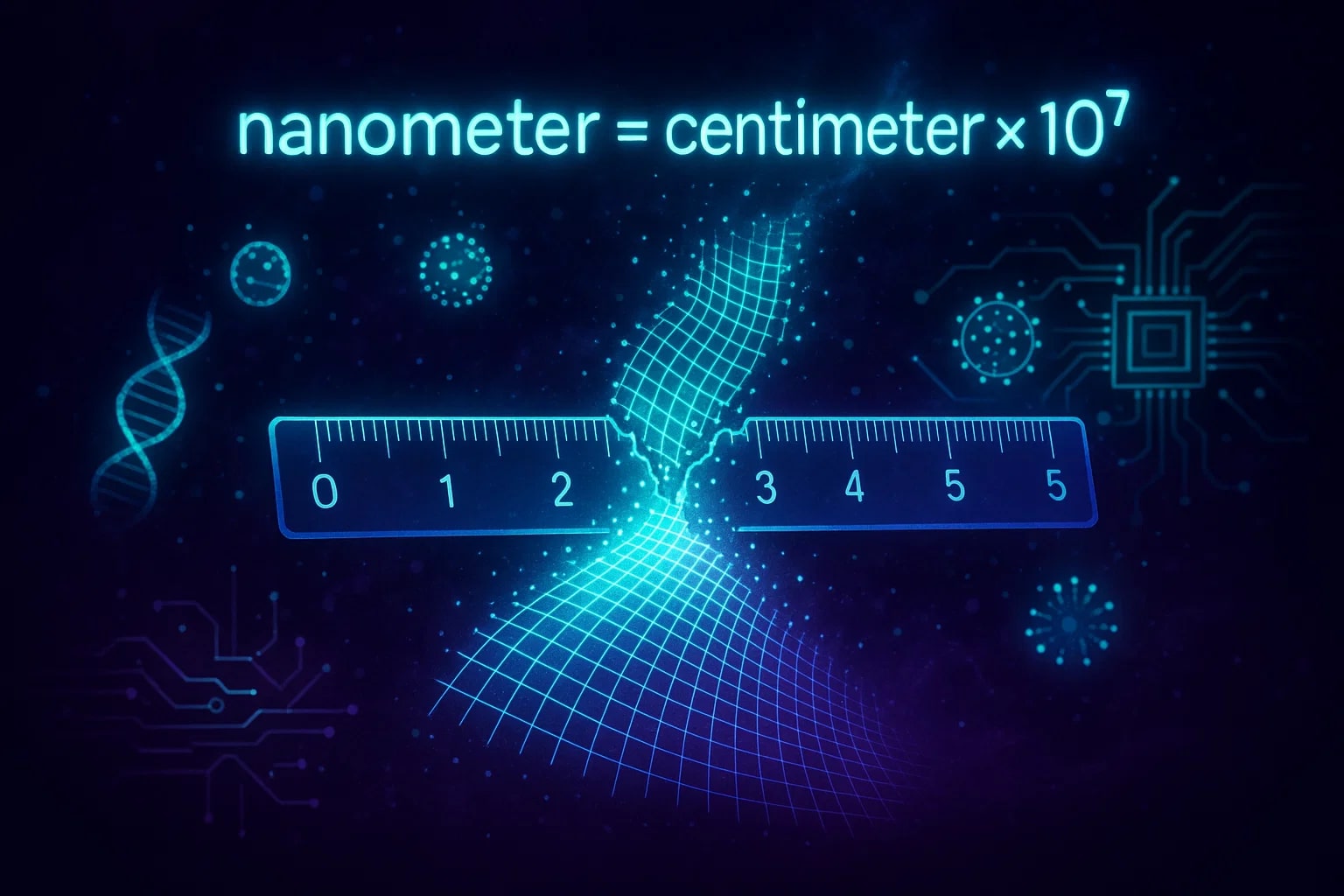
How to Convert cm to nm
The formula is:nanometer = centimeter × 10⁷
Example Conversion
Suppose you want to convert 4 cm into nanometers:nanometer = 4 × 10⁷ = 40 000 000 nm
So, 4 cm = 40 000 000 nm.
This shows how values expand quickly when moving into nanoscopic scales.
For more related conversions, check the Length Converter or explore the complete Conversion Tools collection.
Do you know?
-
The centimeter was introduced in France during the late 18th century as part of the metric system revolution.
-
The nanometer was adopted in the 20th century as physics and biology advanced into microscopic and atomic domains.
-
Visible light wavelengths range from 400 to 700 nm, which explains why nanometers are central to optics and color science.
-
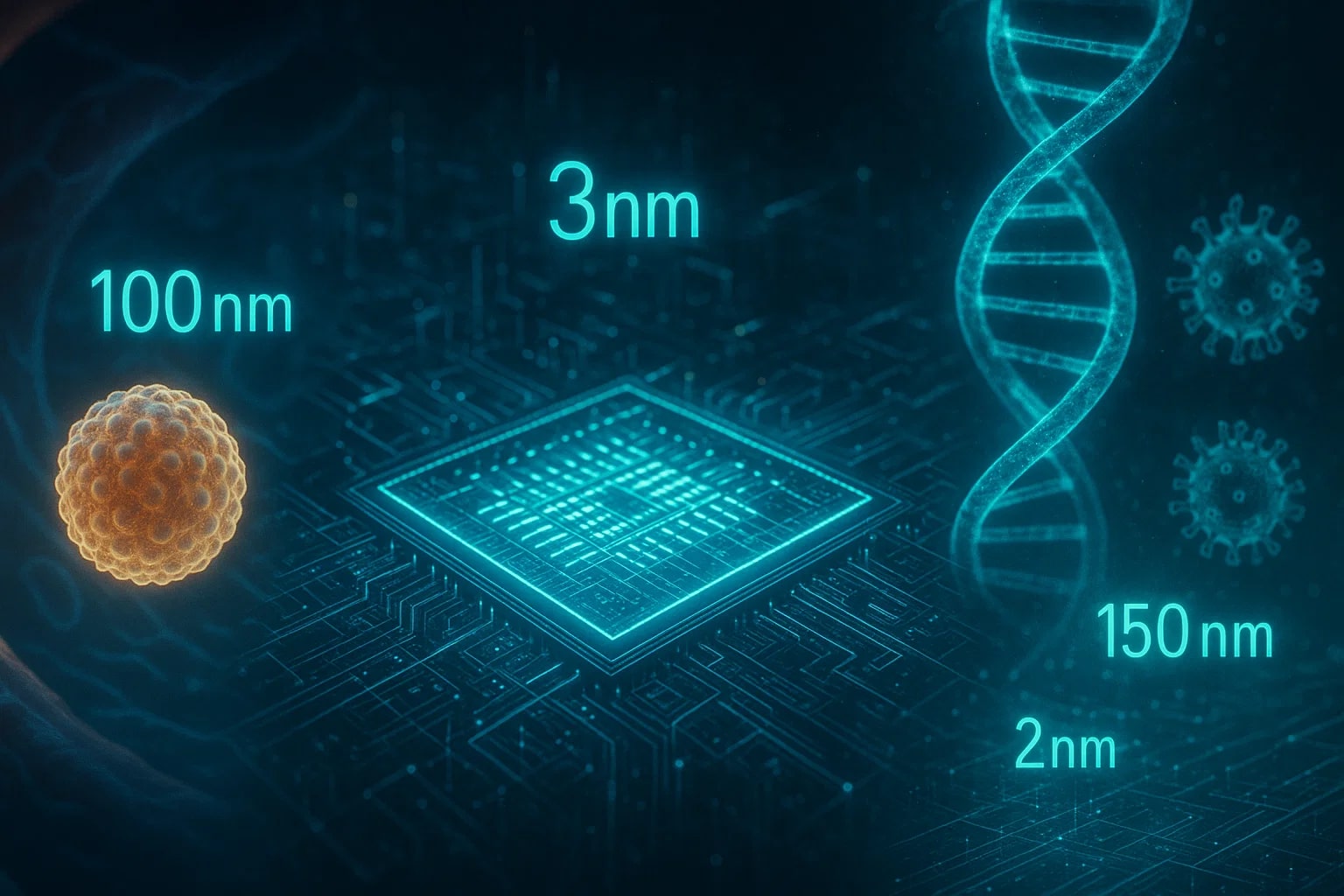
The semiconductor industry often labels generations of chips by their transistor sizes, such as “7 nm” or “5 nm,” showcasing the importance of nanometer-scale engineering.
Nanometers in Modern Technology
In the 1980s, the term nanotechnology entered mainstream science when researchers began to design materials and devices atom by atom. Measuring in nanometers made this field possible. Engineers could describe film thicknesses, nanoparticle sizes, and transistor widths precisely.
For instance, the medical field relies on nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery, often in the 50–200 nm range. In computing, processors built today feature transistors as small as a few nanometers, a scale unimaginable decades ago.
Even biology has embraced nanometers: viruses, proteins, and DNA strands are routinely described in nm, giving scientists a universal language to compare and share discoveries. The shift from centimeters to nanometers may seem extreme, but it captures how science transitions from the familiar to the nearly invisible.
From the Familiar to the Atomic
The conversion from centimeter to nanometer is a reminder of how versatile the metric system is. Centimeters keep life practical and relatable, while nanometers reveal the atomic and molecular structures shaping modern science and technology.
By mastering this simple formula, you can navigate between scales used in everyday life and those shaping tomorrow’s innovations.

