cubic decimeter to cubic centimeter – How to convert dm³ to cm³
The conversion between cubic decimeters and cubic centimeters is a core part of the metric system. Both units measure volume, but they are applied at very different scales. While dm³ is closely linked to liters, cm³ appears in medicine, packaging, and precision science. This guide will walk you through what each unit means, the formula for converting between them, and how they are used in real-world contexts.
What is a cubic decimeter (dm³)?
A cubic decimeter is the volume of a cube with sides of 10 cm. It equals exactly 1 liter. This unit is common in kitchens, packaging, and education, since liters are widely used for daily life measurements such as drinks, cooking ingredients, and storage containers.
What is a cubic centimeter (cm³)?
A cubic centimeter is the volume of a cube with sides of 1 cm. It equals 1 milliliter or 1⁄1000 liter. The cm³ is especially important in healthcare, automotive engineering (engine displacement), and scientific labs where small, precise volumes matter.
Conversion formula – cubic decimeter to cubic centimeter
The relationship is based on simple powers of ten.
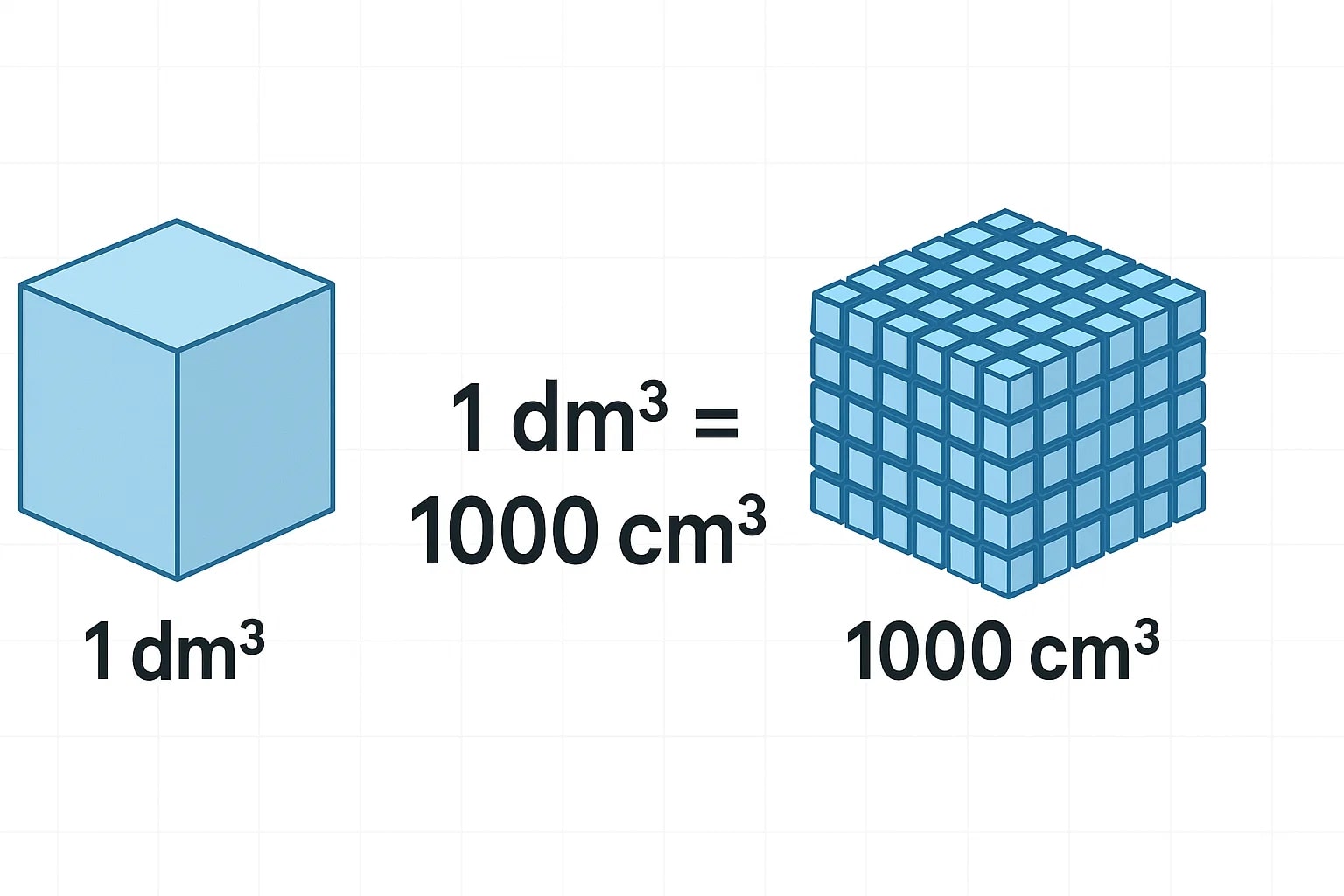
The basic equivalence is:1 dm³ = 1000 cm³
To convert cubic decimeters to cubic centimeters:1 cubic decimeter = cubic centimeter × 1000
To convert cubic centimeters to cubic decimeters:1 cubic centimeter = cubic decimeter ÷ 1000
Examples:
-
2 dm³ = 2000 cm³ -
1500 cm³ = 1.5 dm³
If you want to quickly handle conversions beyond dm³ and cm³, Jetcalculator offers a handy Volume Converter along with a full suite of Conversion Tools designed to make calculations fast and reliable.
Do you know?
-
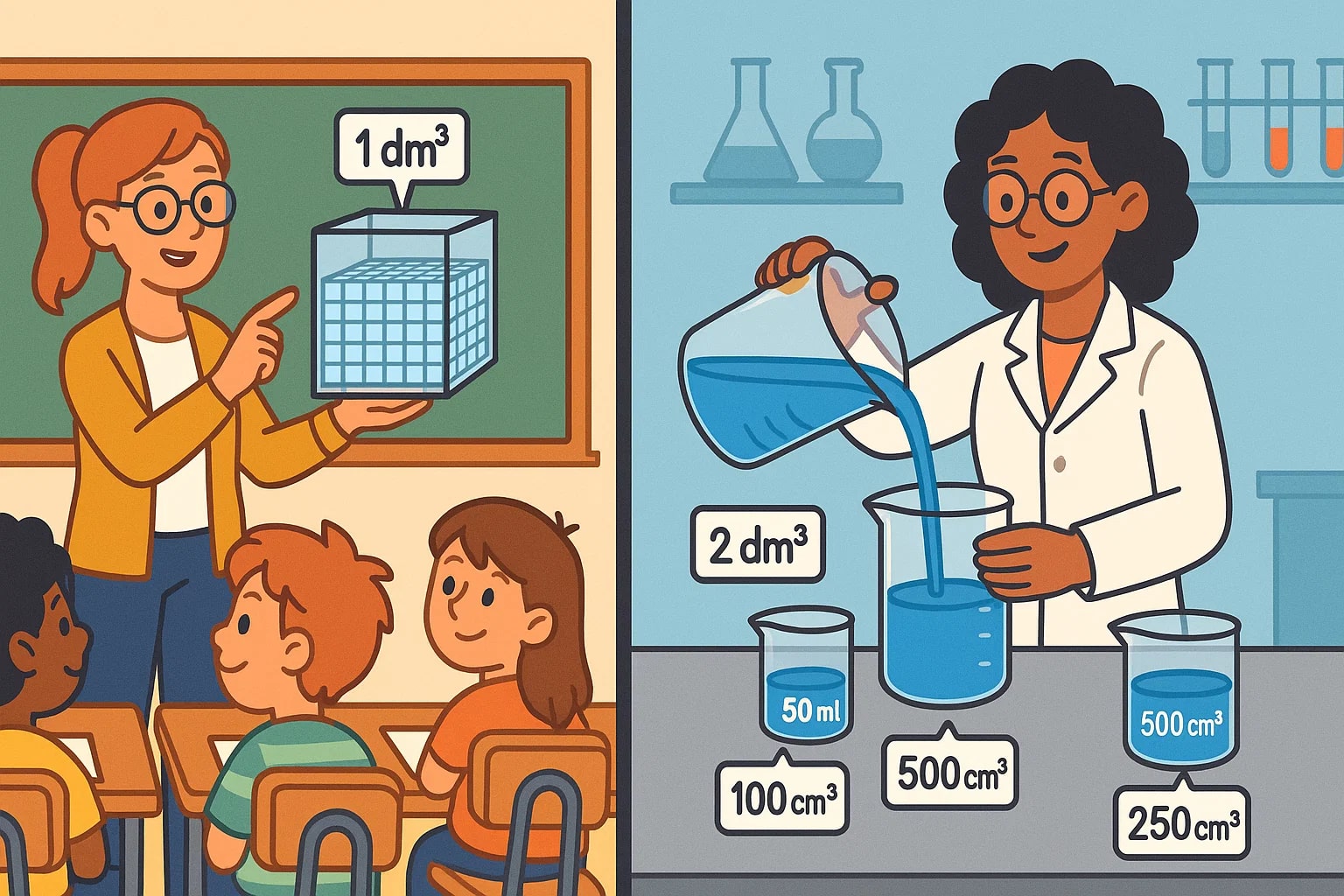
Classroom learning: Teachers often use dm³ cubes in lessons to show how 1 liter equals 1000 cm³. Students can then see the smaller cm³ blocks fitting perfectly inside.
-
Medical detail: A syringe labeled 5 mL is also exactly 5 cm³, showing how interchangeable these two measures are in healthcare.
-
Automotive engineering: Car engine capacity is measured in cm³, while fuel tank size may be described in liters or dm³, making the link between the two essential.
From classrooms to labs – how dm³ and cm³ stay connected
The dm³–cm³ relationship is not just about math, it’s about how people learn and apply knowledge. In schools, a 1 dm³ cube is a common teaching tool to explain liters. Students then measure smaller liquids in cm³ or mL, reinforcing the concept that 1000 cm³ = 1 dm³.
In laboratories, this conversion becomes more than theory. Solutions are prepared in liters or dm³, but exact samples are drawn in cm³. A researcher might create 2 dm³ of solution, then divide it into 2000 cm³ portions for different tests. Without this seamless link, scaling experiments would be much harder.
A bridge across scales
The formula 1 dm³ = 1000 cm³ is a bridge that connects everyday household measures with scientific precision. It shows how a single liter of juice in your fridge can also be expressed as exactly 1000 tiny cubes of 1 cm³ each.
This duality makes the metric system powerful — simple enough for schoolchildren to learn, yet robust enough for engineers, scientists, and doctors. Understanding it means you can move easily between recipes, lab notes, and product packaging without missing a beat.

