decimeter to millimeter – How to convert dm to mm
Moving from decimeter to millimeter shows how flexible and scalable the metric system is. Both units belong to the same decimal ladder, but they represent very different scales. While the decimeter appears mainly in academic contexts, the millimeter is used widely in construction, design, and precision work. Learning how to convert dm to mm helps in both educational exercises and real-world problem solving.
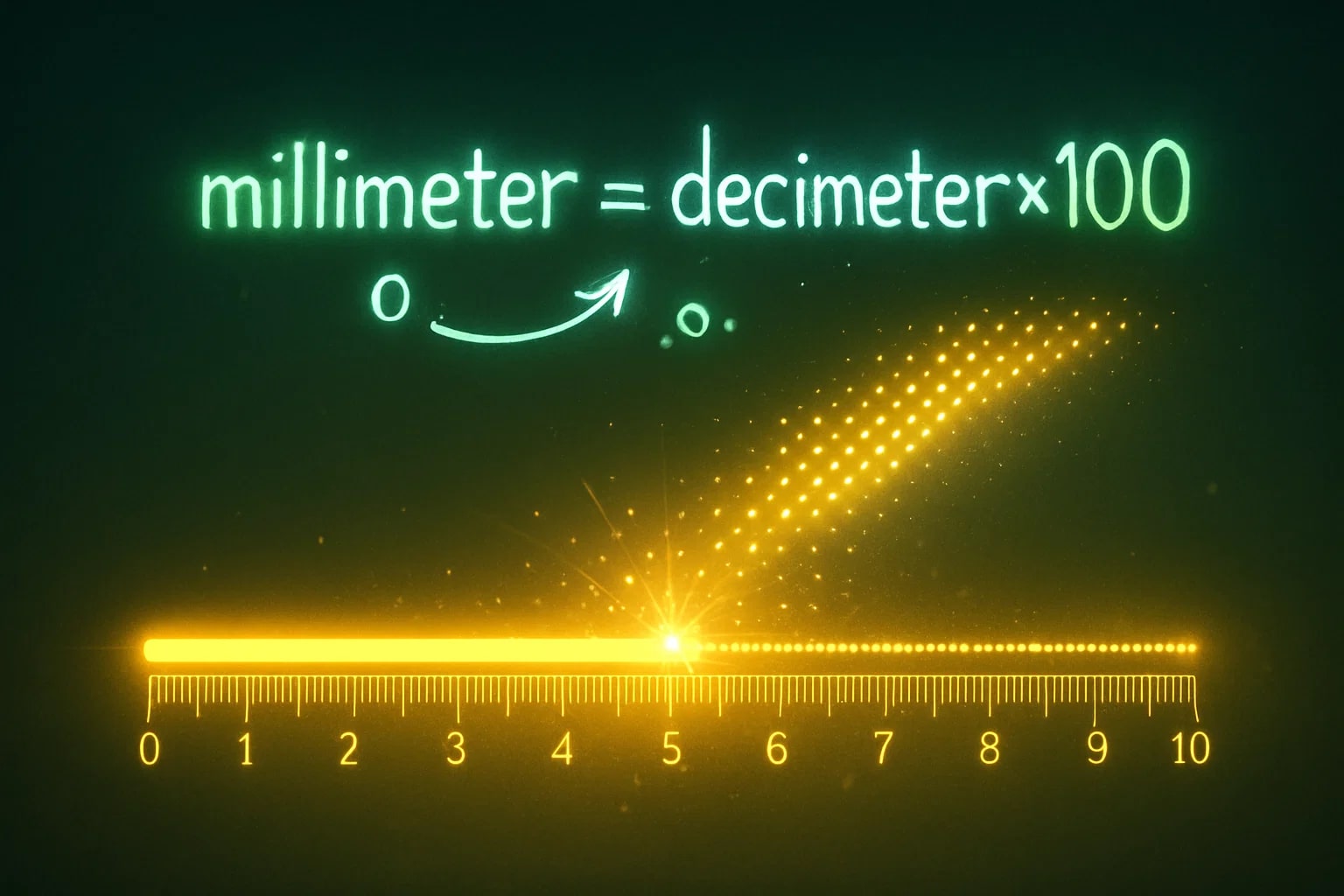
What is a Decimeter (dm)?
A decimeter is one tenth of a meter:
1 dm = 0.1 m.
It equals 10 centimeters or 100 millimeters. Though rarely used in everyday speech, it is valuable in teaching metric relationships.
What is a Millimeter (mm)?
A millimeter is one thousandth of a meter:
1 mm = 0.001 m.
Millimeters are widely used in engineering, carpentry, machining, and daily life wherever small-scale precision is required.
How to Convert dm to mm
The formula is:
millimeter = decimeter × 100
For example, let’s convert 8 dm into millimeters:
millimeter = 8 × 100 = 800 mm
So, 8 dm = 800 mm.
For more conversions, try the Length Converter or explore the broader Conversion Tools collection.
Do you know?
-
The decimeter was introduced with the metric system in the 18th century but is less common in daily use compared to centimeters or meters.
-
Millimeters are widely used in blueprints, technical drawings, and product design, where even small inaccuracies can matter.
-
A standard credit card is about 0.76 mm thick, making millimeters an easy way to describe very thin objects.
-
In rainfall measurements, precipitation is often recorded in millimeters, helping meteorologists give precise reports.
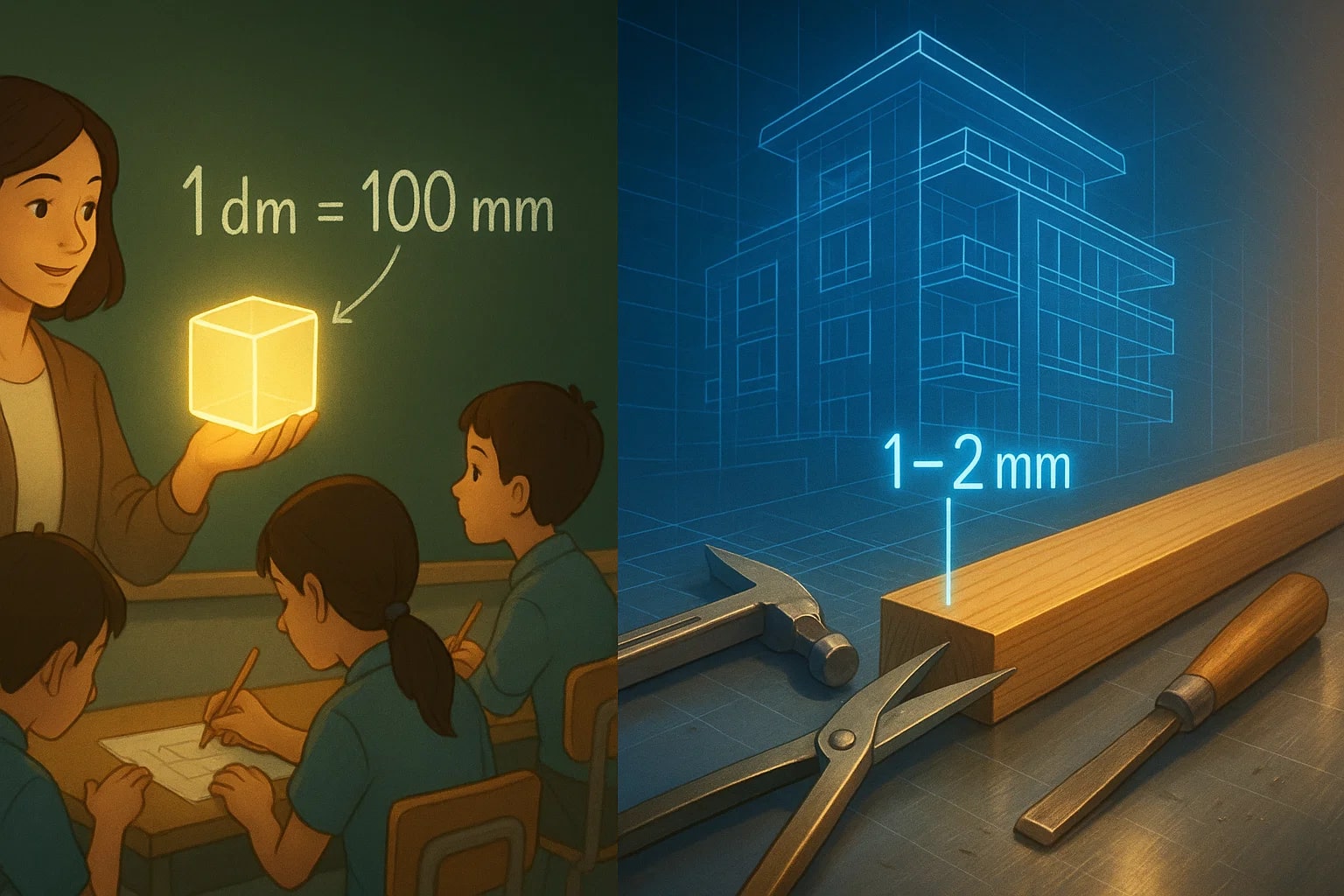
From Classroom Practice to Real Precision
Decimeters often show up in math classes to demonstrate the structure of the metric system. Students quickly learn that scaling up or down simply involves moving the decimal point. Converting to millimeters demonstrates how easily the system handles precision.
In contrast, millimeters are deeply practical in professional life. Architects, engineers, and carpenters rely on them every day. For instance, a design plan may require tolerances of just 1–2 mm, showing how essential this small unit is.
Together, the decimeter and millimeter highlight the versatility of the metric system—one prepares students for conceptual scaling, while the other delivers exactness in the field.
Scaling Down with Confidence
The conversion from decimeter to millimeter demonstrates how effortlessly the metric system spans from medium-sized to highly precise lengths. Though the decimeter is less common outside textbooks, it plays a role in teaching, while the millimeter defines accuracy in countless industries.
By using this simple formula, you can confidently move across these two units and handle measurements in both classrooms and professional settings.

