kilobit to kilobyte – How to convert kbit to kB
When comparing data transfer rates and storage sizes, you'll often run into kilobits and kilobytes — and it’s easy to mix them up. They sound similar and both use the “kilo” prefix, but they represent different things. To compare them properly, you need to convert kilobits (kbit) into kilobytes (kB).
Here’s how the conversion works, along with clear examples and the context behind these two units.
What is a kilobit (kbit)?
A kilobit is a unit of digital data equal to 1,000 bits. It’s most commonly used to measure data transmission speeds. For example, if your internet connection is rated at 512 kbps, that means it can transfer 512,000 bits per second.
You'll find kilobits used in:
-
Streaming bitrate settings
-
Internet bandwidth (e.g. kbps rates)
-
Modem and wireless communication protocols
-
Bluetooth and telemetry systems
Despite being small, kilobits are still useful for understanding how quickly data can move across networks.
What is a kilobyte (kB)?
A kilobyte is a data storage unit equal to 1,000 bytes, or 8,000 bits. It’s a standard measurement for small files and memory allocations. Whether you're saving a document or transferring a low-resolution image, kilobytes are typically the first unit of size you'll see.
Kilobytes appear in:
-
File sizes (e.g. .txt or .html files)
-
Storage space in embedded systems
-
Data usage reports
-
App metadata and update packages
The key difference: kilobits are bits (used in speed), kilobytes are bytes (used in storage).
How to convert kilobit to kilobyte
Since:
1 byte = 8 bits1 kilobyte = 1,000 bytes = 8,000 bits
That means:
1 kilobyte = 8 kilobits
So the formula is:
kilobytes = kilobits ÷ 8
If you prefer decimals:
kilobytes = kilobits × 0.125
A network sends data at 2,400 kilobits per second. To find how many kilobytes that equals:2,400 ÷ 8 = 300 kilobytes per second
An image is compressed to 96 kilobits for fast transmission. To calculate its storage size:96 ÷ 8 = 12 kilobytes
A file download reports 800 kilobits of size — that’s:
800 × 0.125 = 100 kilobytes
For more conversions like this, check out the Data Storage Converter or explore the full Conversion tools section for instant results.

Did you know?
-
Internet speeds are almost always listed in kilobits per second (kbps), but your downloads are measured in kilobytes per second (kB/s) — that's why things can feel slower than expected.
-
An MP3 file encoded at 128 kbps uses about 16 kB of storage per second.
-
The popular SMS (text message) limit of 160 characters typically equals about 140 bytes, or 1.12 kilobits.
-
In early modem days, users downloaded at 56 kbps, which equals just 7 kB/s — it could take 10 minutes to download a single image.
-
Low-power IoT devices often transmit only a few kilobits per second, which is less than 1 kB per second — great for preserving battery life.
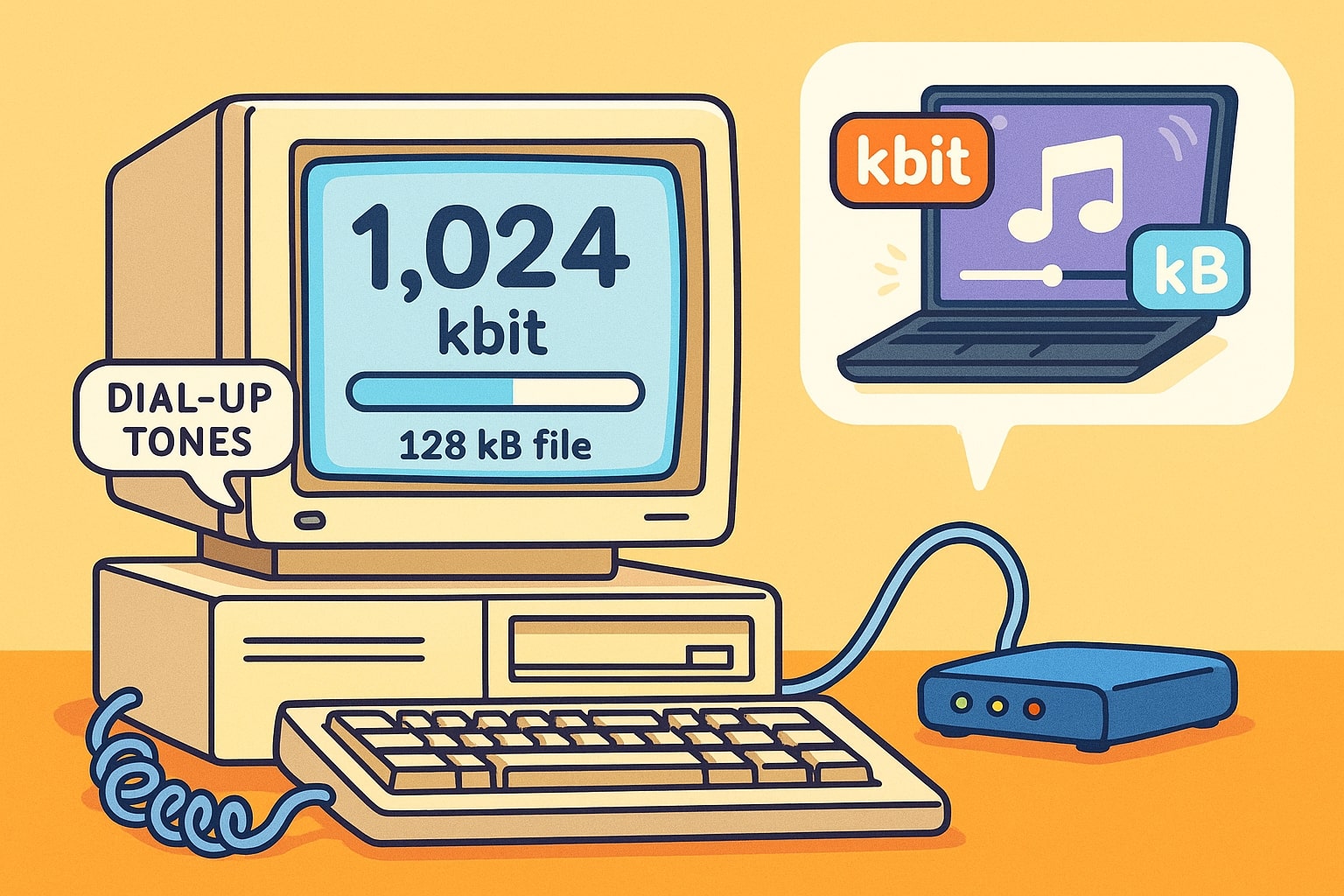
From dial-up tones to download meters – where this conversion still matters
In the 1990s and early 2000s, dial-up connections were rated in kilobits per second, and users had to estimate how long it would take to download kilobyte-sized files. It was common to see a 1,024 kbit file take roughly 128 seconds to download on a 64 kbps connection. Why? Because 1,024 kbit ÷ 8 = 128 kilobytes — the real size of the file.
Even today, this conversion is still relevant. When you're streaming music, downloading attachments, or syncing cloud data, the systems often report speeds in kbit, but your computer saves files in kB. That simple 8:1 ratio helps you bridge the gap between how fast data moves and how much is actually received.
Just divide by 8 — and you're there
Whether you're managing mobile data usage or optimizing file delivery, converting kilobits to kilobytes keeps your expectations realistic and your math clean.
Here’s the quick rule:
kilobytes = kilobits ÷ 8
Need a faster answer? Use our Data Storage Converter or explore more units in Jetcalculator’s full Conversion tools collection.

