Now that you know how to convert mcg to lb, you can easily handle precision weight measurements in scientific research, medicine, or industrial applications. For more versatile unit switches and all-in-one solutions, check out our comprehensive Conversion tool!
How to Convert Micrograms to Pounds?
Weight conversions are essential in science, medicine, and industry. While micrograms (mcg) are used for tiny measurements, pounds (lb) are more common in everyday weight calculations. Understanding how to convert mcg to lb is crucial for accurate weight analysis in various fields. For instant mcg→lb results, try our optimized Weight Converter and get the precision you need!
Micrograms vs. Pounds
-
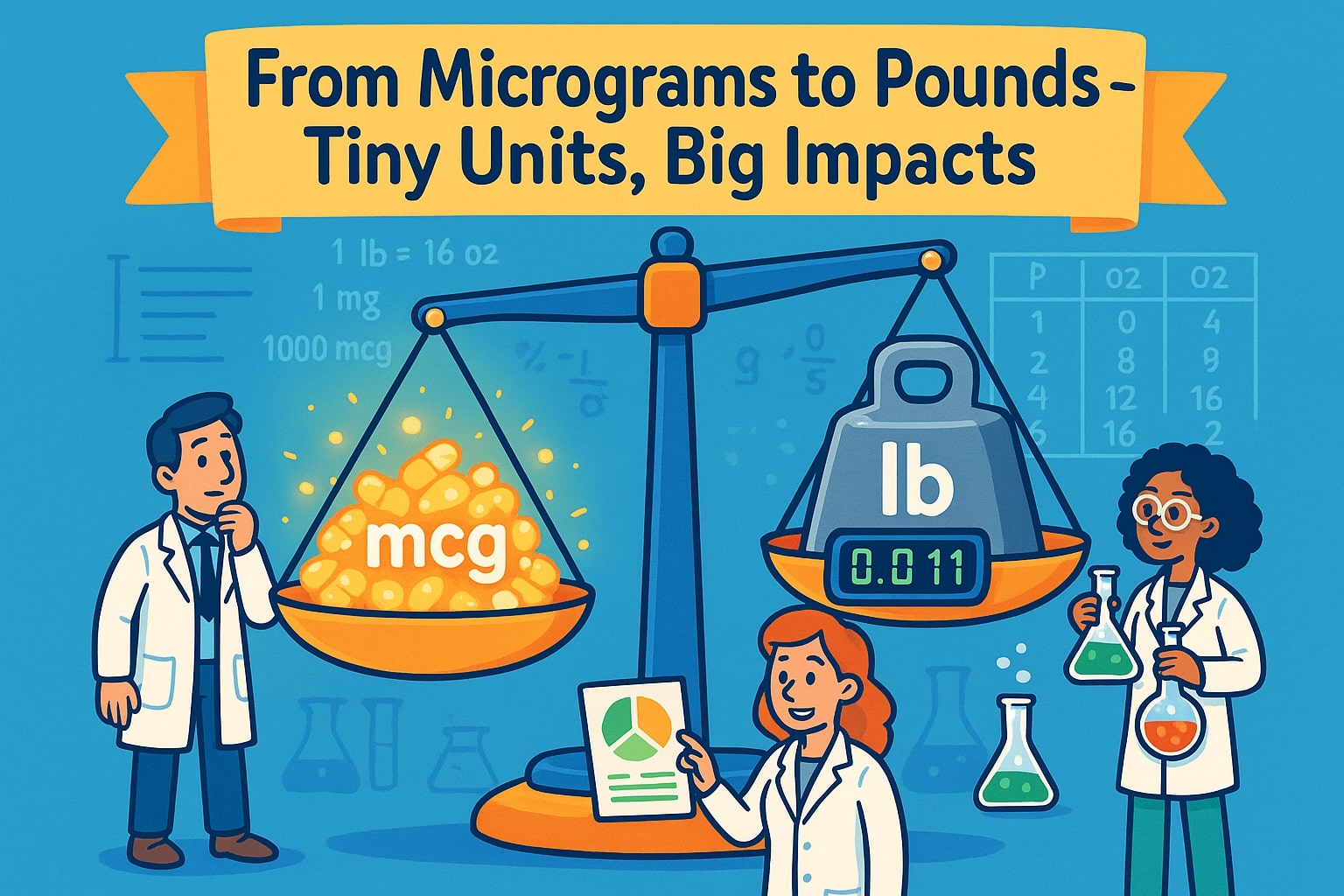
1 pound (lb) = 453,592,370 micrograms (mcg)
-
Micrograms (mcg) are typically used in medicine, nutrition, and chemistry for precise weight measurements.
-
Pounds (lb) are widely used in daily life, sports, and industrial weighing systems.
To convert micrograms to pounds, use this formula:
Pounds (lb) = Micrograms (mcg) ÷ 453,592,370
Example: Convert 5,000,000 mcg to lb
5,000,000 ÷ 453,592,370 ≈ 0.011 lb
This means 5 million micrograms is approximately 0.011 pounds.
Do You Know?
-
A single grain of salt weighs around 60 mcg, meaning you would need 7.5 million grains to equal just 1 pound!
-
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin B12 is about 2.4 mcg, which is over 189 million times smaller than a pound.
-
The smallest insect in the world, the featherwing beetle, weighs only 0.4 mcg—it would take over 1.1 trillion beetles to make up a pound!
-
NASA spacecraft components often weigh only a few mcg to reduce launch weight, ensuring efficiency in space travel.
The Story of the Most Expensive Substance on Earth
One of the rarest and most valuable substances on Earth is antimatter. Scientists estimate that 1 microgram (mcg) of antimatter could cost around $62.5 trillion to produce! This is because creating and storing antimatter requires highly advanced technology and extreme energy levels. Although not yet practical for use, antimatter has the potential to revolutionize space travel and energy production in the future.


