Now that you know how to convert mg to lb, you can apply this knowledge in pharmaceuticals, food measurements, and scientific research. For more versatile unit switching—across weights, lengths, volumes, and beyond—explore our comprehensive Conversion tool and make every calculation effortless!
How to convert milligrams to pounds?
Converting mg to lb is essential in fields like pharmaceuticals, food science, and chemistry, where precise weight measurements matter. Since milligrams (mg) and pounds (lb) belong to different measurement systems—metric and imperial—knowing how to switch between them ensures accuracy every time. For instant, user-friendly conversions—whether you’re dosing medications or scaling recipes—try our intuitive Weight Converter and get your result in a flash!
Milligrams vs. Pounds
-
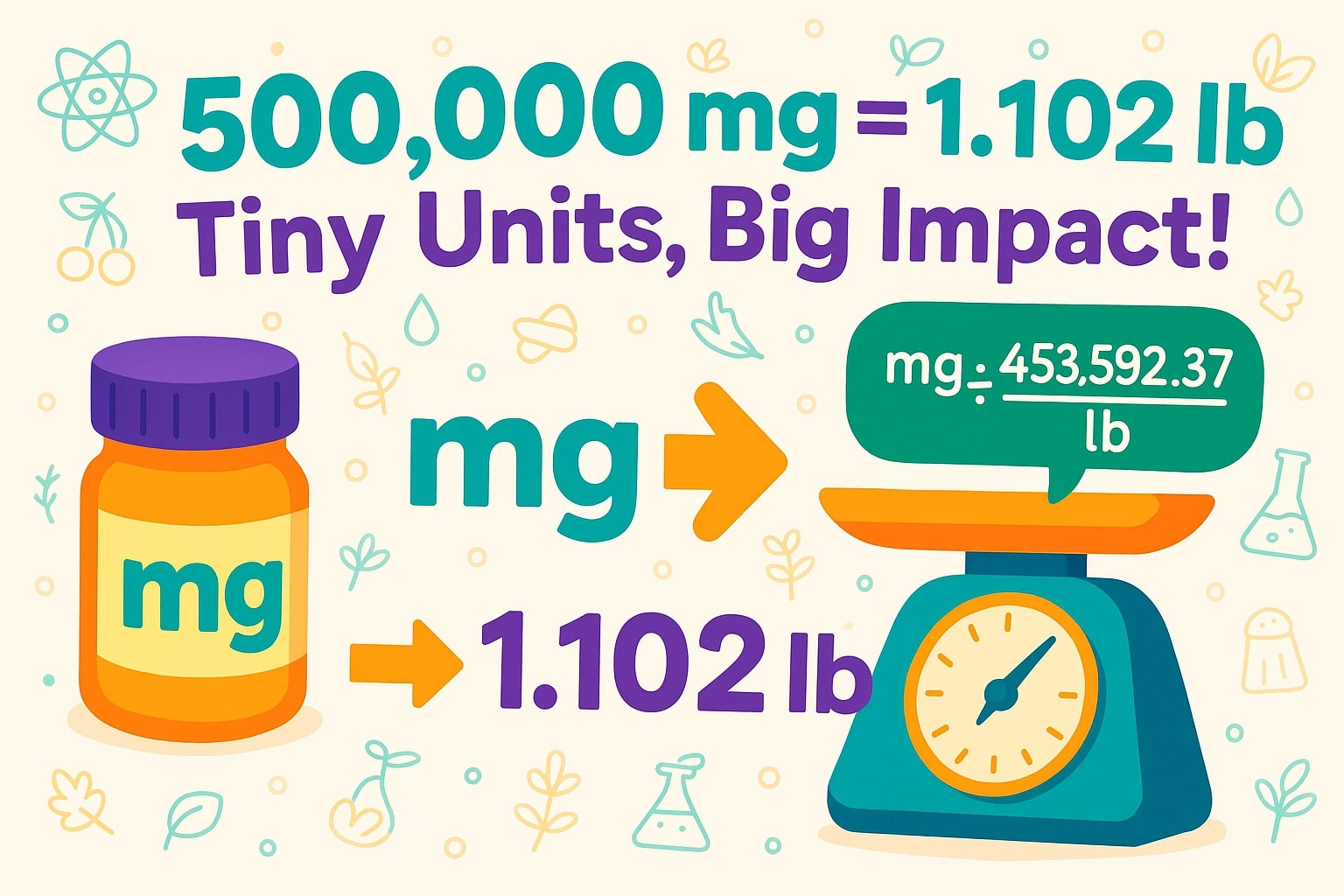
1 pound (lb) = 453,592.37 milligrams (mg)
-
Milligrams (mg) measure small weights, commonly used for medications, supplements, and chemical substances.
To convert milligrams to pounds, use this formula:
Pounds (lb) = Milligrams (mg) ÷ 453,592.37
Example: Convert 500,000 mg to pounds:
500,000 ÷ 453,592.37 = 1.102 lb
Did You Know?
-
A standard aspirin tablet contains about 325 mg of the active ingredient.
-
A single coffee bean weighs around 132 mg.
-
The smallest known mammal, the bumblebee bat, weighs approximately 2 grams (2,000 mg).
-
The average human brain weighs about 3 lb (1,361,777 mg).
-
A grain of sand typically weighs 50 to 100 mg.
The 500-Milligram Moon Dust That Changed History
During the Apollo 11 mission in 1969, astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin collected moon rock and moon dust samples weighing just a few milligrams to grams. One of the most fascinating discoveries was that 500 mg of moon dust contained elements found on Earth, proving that planetary bodies share some common materials.
These precious moon dust samples, weighing far less than a pound, helped scientists understand the composition of the Moon and its potential for future exploration. Today, NASA and private companies continue to study lunar samples for future moon missions and resource extraction.


