Newton to Millinewton – How to change N to mN
Converting newton to millinewton is common when dealing with extremely light forces in laboratories, micro‑devices, and precision testing. Here’s what these two force units represent, how to calculate their relationship, and why engineers rely on them for accuracy.

What is a newton (N)?
The newton (N) is the SI standard unit of force, defined as the force required to accelerate a 1 kg mass at 1 m/s². It is widely used in mechanics, physics, and industrial measurements, from analyzing loads on machinery to studying how objects move.
To put it simply, Earth’s gravity pulls on a 1 kg object with roughly 9.8 N of force.
What is a millinewton (mN)?
A millinewton (mN) is a smaller force unit, equal to one‑thousandth of a newton (1 N = 1 000 mN). The “milli‑” prefix means ¹⁄₁₀₀₀, making it useful in fields where delicate measurements are essential — such as biomedical research, surface testing, and precision robotics.
For instance, sensors measuring the tension in thin biological tissues often record forces in the range of just a few mN.
Conversion formula
Switching between these units is simple thanks to their decimal relationship:
1 N = 1 000 mN
Force (mN) = Force (N) × 1 000
Example:
A test probe applies ¾ N of pressure to a soft material. Converting this to millinewtons:
¾ N × 1 000 = 750 mN.
So, ¾ N = 750 mN.
Need other conversions? Visit Conversion tools or, for calculations involving other dimensions, check the Force Converter.
Did you know?
-
The contact force of a single eyelash brushing against skin is about 0.5–1 mN.
-
Many medical catheters are tested for flexibility using loads as small as 20 mN.
-
In robotic grippers, gripping force for small electronic parts often stays below 100 mN to prevent damage.
-
Advanced tribology studies (friction and wear) regularly measure forces in the mN range for coatings and lubricants.
-
10 mN is approximately the downward weight of 1 g under standard gravity.
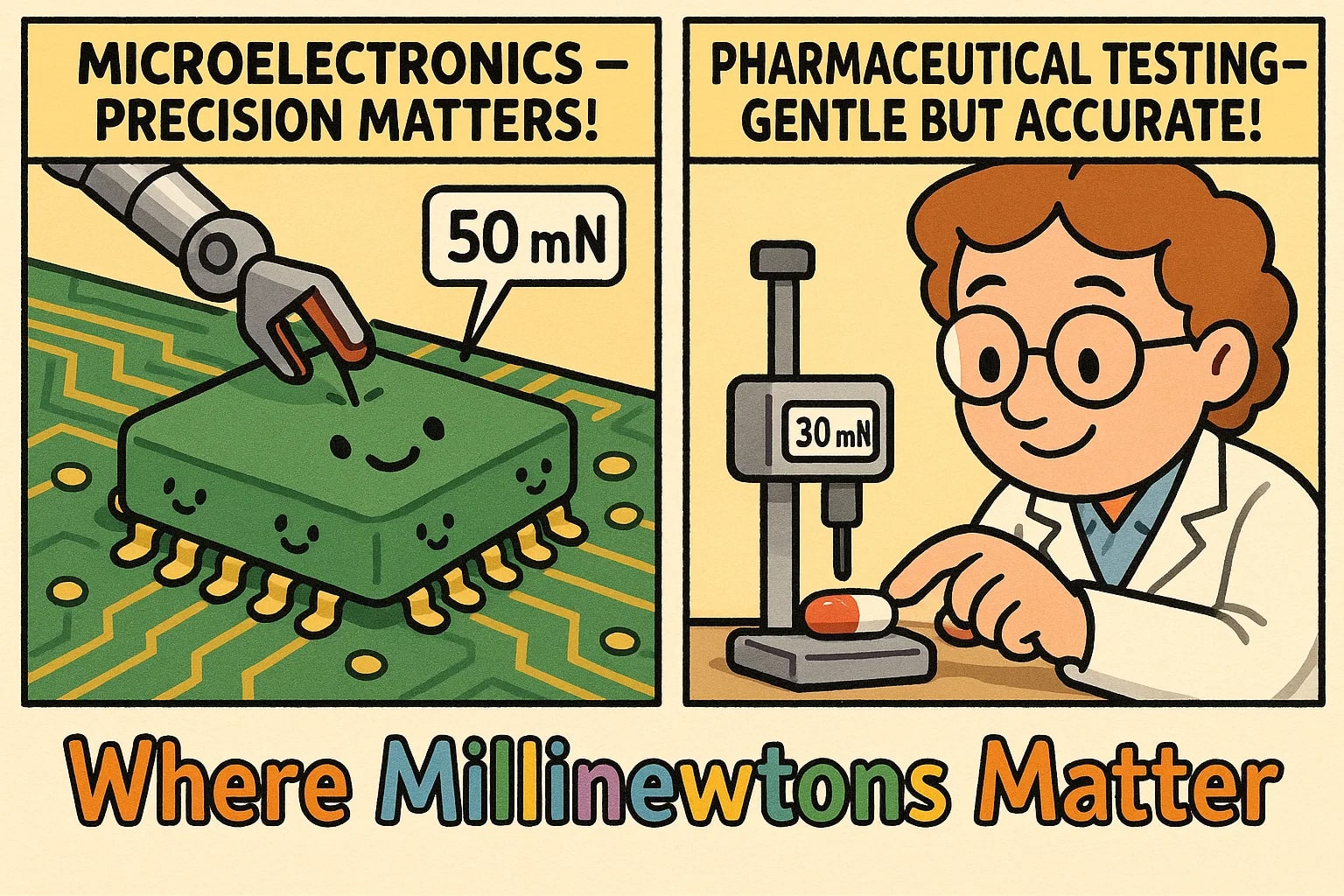
Precision in Action: Where Millinewtons Matter
While newtons work well for most physical and industrial applications, millinewtons give researchers and engineers a finer lens for small‑scale work.
In microelectronics, millinewton readings are crucial when testing solder joint integrity, where just 50 mN can indicate a weak connection. In pharmaceutical labs, millinewton forces help analyze tablet hardness without crushing fragile samples.
By using mN rather than decimals like 0.05 N, technical teams can report results cleanly and avoid rounding errors.
Converting for Micro‑Scale Clarity
Expressing small forces in millinewtons isn’t just neat — it reduces mistakes and improves readability in reports. Instead of writing 0.003 N, you can write 3 mN and make your data clear at a glance.
Jetcalculator simplifies every step. Use our Conversion tools or explore the Force Converter if you’re working with multiple units in complex designs.
From testing a soft polymer’s strength to calibrating sensitive lab equipment, converting newton to millinewton ensures your results remain precise and easy to communicate.

