hectopascal to pascal – How to convert hPa to Pa
Converting hectopascal to pascal is simple but essential in science, weather forecasting, and engineering. The pascal (Pa) is the SI unit of pressure, while the hectopascal (hPa) is commonly used in meteorology to describe atmospheric pressure. Jetcalculator’s converter gives instant results, but let’s explore what these units mean, how to convert them, and why they matter.
What is a Hectopascal (hPa)?
A hectopascal (hPa) equals 100 pascals. The prefix “hecto” means one hundred. In meteorology, hPa is the standard unit for atmospheric pressure, replacing the older “millibar.” For example, typical sea-level pressure is about 1013 hPa.
What is a Pascal (Pa)?
A pascal (Pa) is the SI unit of pressure, defined as one newton per square meter (N/m²). It is widely used in physics, engineering, and material science. However, because the pascal is small, multiples such as kPa, hPa, or MPa are often used in practice.
Formula to Convert hPa to Pa
The relationship is straightforward:
-
1 hPa = 100 Pa -
1 Pa = 0.01 hPa
So the formulas are:
-
P (Pa) = P (hPa) × 100 -
P (hPa) = P (Pa) ÷ 100
Example: 1013 hPa = 101,300 Pa.
With Jetcalculator’s hectopascal to pascal converter, you can calculate instantly without manual work.
Did you know?
-
Hectopascal fact: The unit hPa is used by meteorologists worldwide. Aviation weather reports list pressure in hPa so pilots can set their altimeters.
-
Pascal fact: The pascal is named after Blaise Pascal, a 17th-century French mathematician and physicist who studied fluid mechanics and pressure.
-
Hectopascal fact: The record low atmospheric pressure measured in a tropical cyclone was 870 hPa during Typhoon Tip in 1979.
-
Pascal fact: Human blood pressure is about 16,000 Pa (systolic), much higher than normal atmospheric pressure in pascals.
Weather Forecasting
One of the most important uses of hPa and Pa is in weather science. Meteorologists rely on hectopascals to track changes in air pressure, which are critical for predicting storms and fair weather.
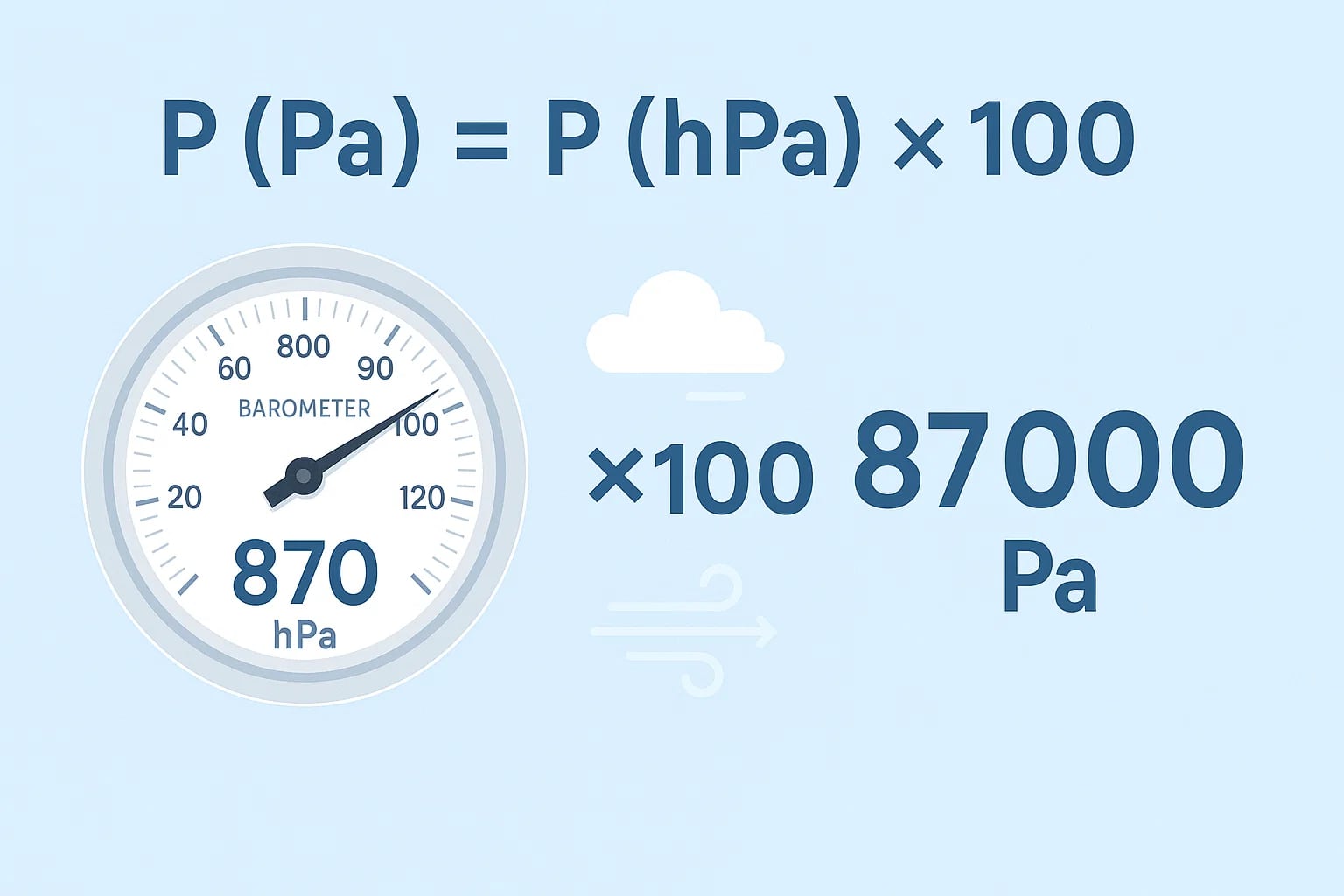
For example, when atmospheric pressure drops from 1013 hPa to below 1000 hPa, it often signals stormy conditions. In severe cyclones, pressure can fall dramatically, as low as 870 hPa. Converting this into pascals makes the scale even clearer:
870 hPa × 100 = 87,000 Pa.
This precision helps scientists compare atmospheric data with other pressure measurements in physics and engineering.
In aviation, pilots use weather charts measured in hPa to adjust their altimeters. A small error in pressure conversion could result in incorrect altitude readings, which shows why knowing the exact relationship between hPa and Pa is vital.
Thus, the conversion between these two units is not just theoretical—it plays a direct role in predicting weather, ensuring aviation safety, and preparing for natural disasters.

Simple Conversion, Global Impact
The conversion 1 hPa = 100 Pa may be straightforward, but its impact is vast. From weather forecasting and aviation to engineering and science, the link between hectopascal to pascal keeps measurements consistent and accurate.
Jetcalculator’s hectopascal to pascal converter makes it effortless to get quick results. For broader needs, try our Pressure Converter or explore the full set of Conversion Tools to handle all your calculations confidently.

