milliwatt to watt (mW to W) - How to convert mW to W
Converting milliwatt to watt is essential in electronics, medical devices, and scientific applications. Milliwatts are used when measuring extremely low power, while watts are applied to everyday household devices. This conversion bridges the world of micro-scale energy with the scale of daily life.
What is a Milliwatt?
The milliwatt (mW) is a unit of power equal to 0.001 W. It’s commonly used in electronics, lasers, and communications. For example, a smartphone microphone or wireless earbud may operate using only a few milliwatts. This small unit helps engineers measure efficiency in devices where every fraction of power matters.
What is a Watt?
The watt (W) is the SI unit of power, named after James Watt. It equals one joule of energy per second. From LED light bulbs rated at 5–15 W to laptops consuming 60–100 W, the watt is the standard way to measure energy usage in daily life.
Formula: Convert mW to W
The relationship is simple:
1 mW = 0.001 W
Example:
If a laser pointer uses 25 mW, then:
25 × 0.001 = 0.025 W
This shows how a small milliwatt-level device translates into fractional watts.
For quick calculations, our Conversion Tools provide instant results for milliwatts, watts, and many other units.
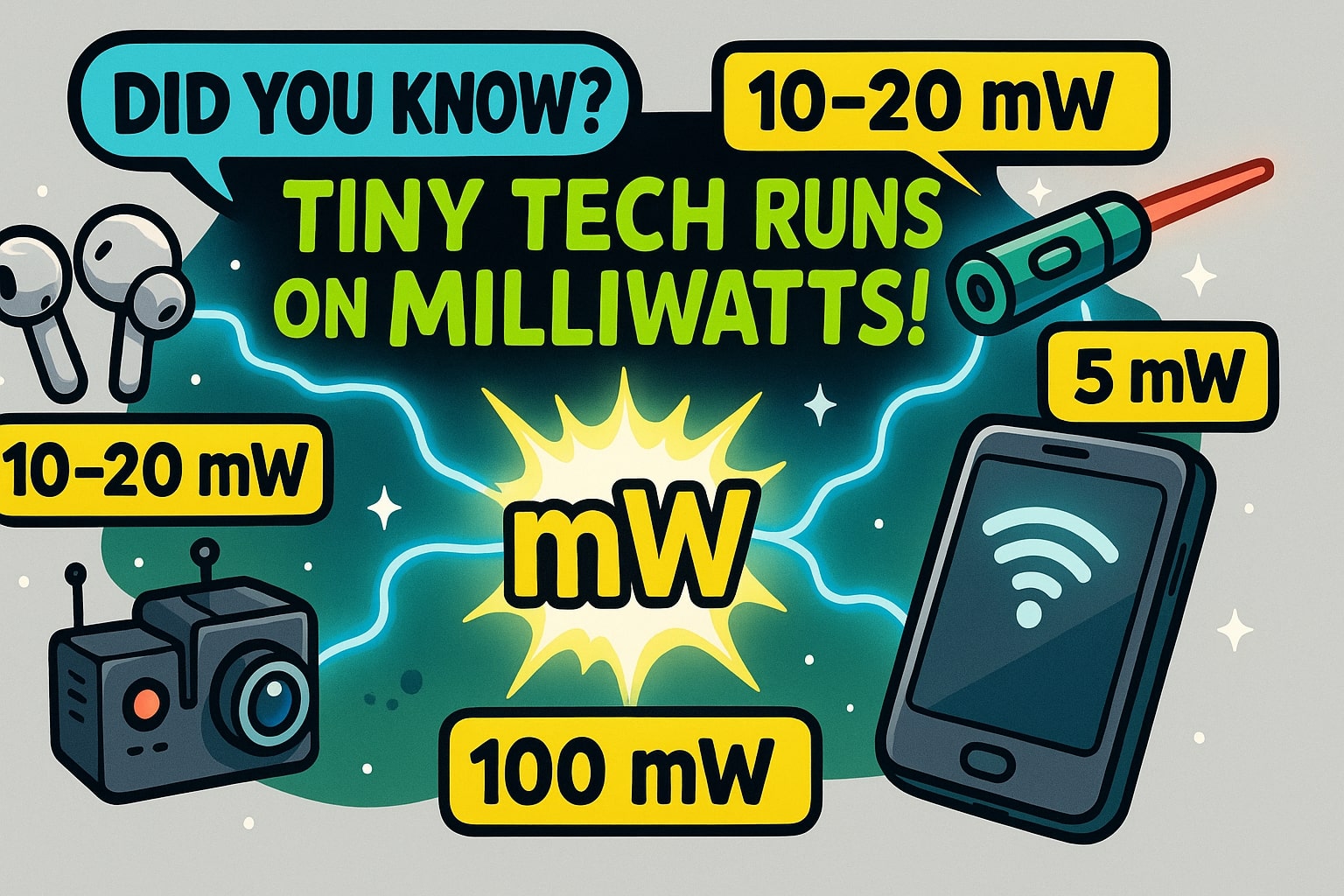
Did you know?
-
A typical Bluetooth earbud consumes around 10–20 mW, allowing long battery life despite its tiny size.
-
Laser pointers for classroom use are often rated at 5 mW, staying within safety standards.
-
In popular culture, spy gadgets in films like Mission Impossible often highlight micro-sized tech running on milliwatt levels.
-
The Wi-Fi transmitter in your phone usually operates around 100 mW, balancing power with efficiency to extend battery life.
From Micro Power to Everyday Energy
The story of milliwatts is the story of miniaturization. In the 1970s, early portable music players and calculators ran on watt-level batteries, limiting their size and portability. But as technology advanced, engineers designed chips and circuits that consumed only milliwatts of power.
A striking example is the rise of hearing aids. Early models required bulky batteries and frequent replacements, consuming several watts. Today, modern digital hearing aids run on just a few milliwatts, delivering clearer sound with far less energy. This shift not only improved comfort but also extended battery life, allowing millions of people to use them daily with ease.
This transformation—from watts to milliwatts—reflects how technology continues to shrink while becoming more powerful. Milliwatts keep our smallest gadgets running, while watts power the devices we rely on every day.
Small Numbers, Big Impact: The Value of milliwatt to watt
Accurate conversions are important for engineers, students, and tech enthusiasts. Alongside milliwatt to watt, our Power Converter supports a full range of energy units, from microwatts to megawatts. Paired with the all-in-one Conversion Tools, these calculators make scaling power values simple and reliable.
The conversion from milliwatt to watt (mW to W) is as simple as multiplying by 0.001, but its meaning is far-reaching. Milliwatts define the world of microelectronics and efficiency, while watts bring energy into the devices of everyday life. With Jetcalculator, you can connect both scales with ease and confidence.

