terabit to gigabyte – How to convert Tbit to GB
When you’re working at the scale of terabits, you’re likely dealing with serious data — enterprise-grade transfers, data centers, or backbone-level networks. But most people think in gigabytes, the more familiar storage unit. If you're trying to understand how fast transfers translate into usable storage, converting terabits (Tbit) to gigabytes (GB) gives you a clearer view.
This guide shows you exactly how to make that conversion — with examples and real-world relevance.
What is a terabit (Tbit)?
A terabit equals 1,000,000,000,000 bits, or 1 trillion bits. It’s part of the decimal system (SI units), commonly used in large-scale telecommunications and high-speed data links.
You’ll see terabits used in:
-
Fiber-optic backbone internet systems
-
Core router throughput
-
Satellite communication specs
-
Hyperscale data replication and CDN transfer speeds
While bits are ideal for measuring continuous flow (like internet speed), they’re not often used for storage.
What is a gigabyte (GB)?
A gigabyte equals 1,000,000,000 bytes, or 8,000,000,000 bits (since 1 byte = 8 bits). Gigabytes are the standard unit for measuring:
-
File and folder sizes
-
Flash drive and SSD capacities
-
App and OS installations
-
Data caps and cloud storage plans
The conversion from bits to bytes — and from terabits to gigabytes — helps bridge the gap between data movement and data storage.
How to convert terabit to gigabyte
Here’s the math in two steps:
1 byte = 8 bits
1 gigabyte = 1,000,000,000 bytes = 8,000,000,000 bits
1 terabit = 1,000,000,000,000 bits
So the formula is:
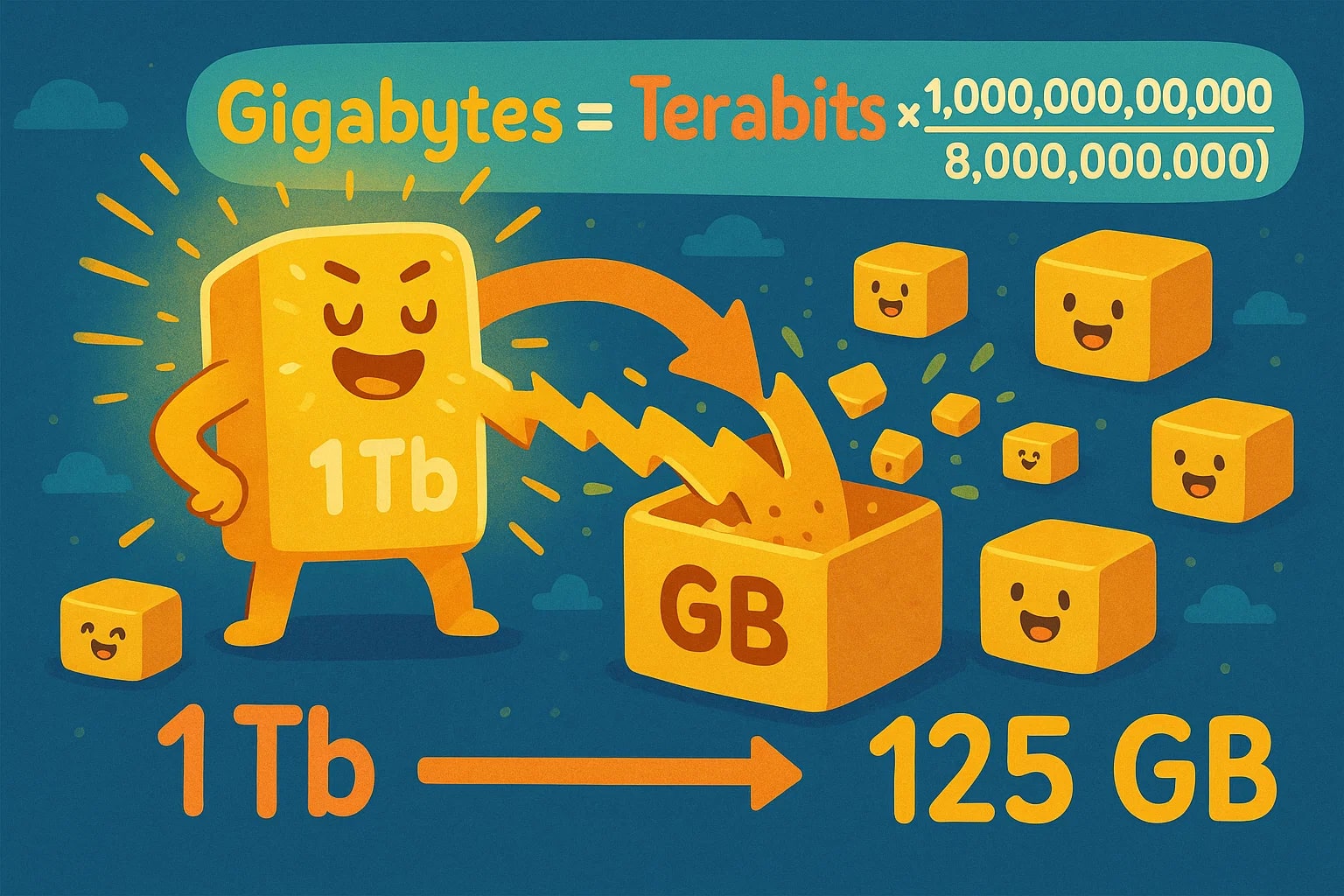
gigabytes = terabits × (1,000,000,000,000 ÷ 8,000,000,000)
which simplifies to:
gigabytes = terabits × 125
You’re handling a data stream of 4 terabits — how much storage is that in GB?
4 × 125 = 500 gigabytes
A server transfers 0.8 terabits of information during a backup job:
0.8 × 125 = 100 gigabytes
You’re moving a dataset across two data centers with a throughput of 10 Tbit:
10 × 125 = 1,250 gigabytes
To do more calculations instantly, try our Data Storage Converter or explore additional formats in the full Conversion tools collection.
Did you know?
-
Global fiber backbones can handle multiple terabits per second, especially between major cities or countries.
-
A 1 Tbit transfer could hold over 150 hours of HD video, assuming standard compression and encoding.
-
In 2021, the average global internet traffic exceeded 1.2 terabits per second during peak hours — that’s 150 GB per second.
-
Cloud platforms like AWS and Google Cloud often replicate entire data volumes in terabit chunks, especially for failover or backup.
-
In 5G and future 6G networks, core systems will routinely deal with terabit-level backbone throughput, while users still think in gigabytes.
Where big data meets real-world storage
At the core of high-speed networks and modern computing infrastructure lies a constant challenge: moving massive amounts of data quickly. A terabit describes how fast that data flows — but a gigabyte tells you how much you actually need to store.
When the Fujitsu K computer was installed in Japan, one of its core requirements was to stream terabits of data across internal nodes. Translating those rates into gigabytes helped engineers allocate buffer memory, build cooling systems, and optimize software architecture.
And in modern applications, from AI model training to real-time analytics, converting terabit speeds into gigabyte storage gives developers a working picture of what systems can handle — and how much they need to scale.

Multiply by 125 — and bridge the gap
When you're translating between transfer rates and file sizes, it’s helpful to remember:
gigabytes = terabits × 125
This gives you a fast way to turn high-speed data into real-world storage requirements. Whether you're planning a backup, designing a fiber network, or comparing cloud sync speeds, this simple conversion keeps your metrics aligned.
Need help with more units? Try our Data Storage Converter or check out Jetcalculator’s full library of Conversion tools.

