watt to milliwatt (W to mW) - How to convert W to mW
Converting watt to milliwatt is a simple but essential calculation in electronics, medical devices, and modern gadgets. While watts measure the power of everyday devices, milliwatts are used for precision equipment and energy-efficient technology. This conversion links the energy of household items to the delicate demands of microelectronics.

What is a Watt?
The watt (W) is the SI unit of power, equal to one joule per second. It describes the actual energy consumed by a device. Everyday examples include a 60 W light bulb, a 1000 W microwave, or a 2000 W heater. Watts are practical for larger devices and appliances used in homes and industries.
What is a Milliwatt?
The milliwatt (mW) is a much smaller unit of power equal to 0.001 W. It’s commonly used in electronics, telecommunications, and laser technology. For example, Bluetooth transmitters, phone microphones, and hearing aids often operate in the 10–100 mW range.
Formula: Convert W to mW
The formula is straightforward:
1 W = 1000 mW
Example:
If a small sensor uses 0.05 W:
0.05 × 1000 = 50 mW
This shows how even a fraction of a watt translates into dozens of milliwatts in sensitive electronics.
For instant results, our Conversion Tools make it quick and precise, saving time for both professionals and students.
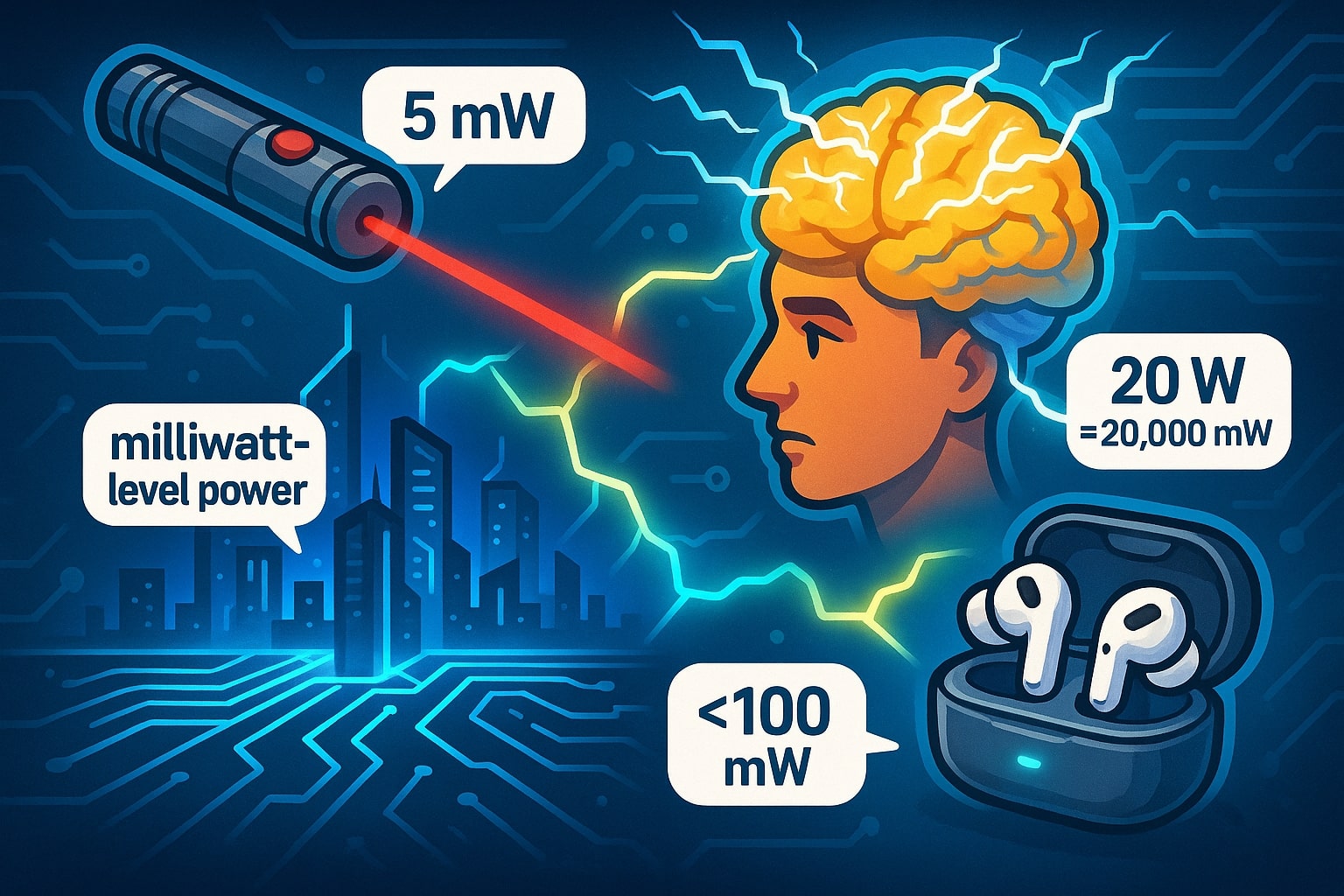
Did you know?
-
A laser pointer used in classrooms often operates at around 5 mW, staying within safe limits.
-
The human brain consumes about 20 W of power, which equals 20 000 mW—tiny compared to a household appliance but massive compared to micro devices.
-
In films like Tron, futuristic digital worlds are often depicted with glowing circuits—those glowing lines would actually run on milliwatt-level power in reality.
-
Wireless earbuds consume less than 100 mW, which is why they can run for hours on tiny batteries.
From Light Bulbs to Wearables
In the 20th century, watts dominated the conversation about power—bulbs, radios, and appliances were all marketed with watt ratings. But as technology shrank, the focus shifted to milliwatts.
A clear example is the evolution of portable music players. Early cassette players in the 1980s consumed several watts of power, requiring bulky batteries. Fast forward to today, and wireless earbuds deliver higher-quality sound while consuming less than 50 mW each. This leap in efficiency was made possible by advances in microelectronics.
The transition from watts to milliwatts reflects the larger story of technology: making devices smaller, smarter, and more energy-efficient. What once required watts of energy can now be achieved in milliwatts, changing how we interact with gadgets daily.
Tiny Numbers, Huge Innovations
Accurate conversion from watt to milliwatt is essential for engineers, students, and tech enthusiasts working on projects from IoT devices to wearable technology. Alongside W to mW, our Power Converter supports all major units, from microwatts to megawatts. Pair it with the all-in-one Conversion Tools to cover every energy calculation seamlessly.
The conversion from watt to milliwatt (W to mW) is as simple as multiplying by 1000, but its significance is enormous. Watts power the larger devices we rely on, while milliwatts sustain the miniature technologies driving modern innovation. With Jetcalculator, you can move smoothly between these scales and see how small power values are making a huge impact in the real world.

