watt to volt ampere (W to VA) - How to convert W to VA
Converting watt to volt ampere is essential in electrical engineering, UPS systems, and power planning. Watts (W) measure real, usable power, while volt amperes (VA) represent apparent power. This conversion helps you calculate the efficiency of your system and avoid overloading.
What is a Watt?
The watt (W) is the SI unit of real power, equal to one joule per second. It describes the actual energy consumed or produced by a device. For example, a 60 W light bulb uses 60 joules of energy per second. Real power is what truly performs useful work—heating, lighting, or running motors.
What is a Volt Ampere?
The volt ampere (VA) is a unit of apparent power. It combines both real power (W) and reactive power (kVAr). Devices like UPS units, transformers, and generators are often rated in VA because it indicates the maximum load they can handle before accounting for efficiency losses.
Formula: Convert W to VA
The conversion depends on the power factor (PF), which measures how effectively electrical power is converted into useful work. The formula is:
VA = W ÷ PF
Example:
If a computer consumes 400 W and operates at a power factor of 0.8:
400 ÷ 0.8 = 500 VA
So, the computer requires 500 VA of apparent power capacity to run reliably.
Did you know?
-
Most residential appliances have a power factor close to 1, meaning W ≈ VA.
-
Servers and data centers often run with PF values around 0.9–0.95 to maximize efficiency and reduce wasted energy.
-
In pop culture, exaggerated power figures appear in movies like Iron Man, where Tony Stark’s arc reactor supposedly produced gigawatts—far beyond realistic watt/VA conversions.
-
Businesses often oversize their UPS systems because they forget to account for PF when converting watts to volt amperes.
Power Factor Lessons: A Story from the Server Room
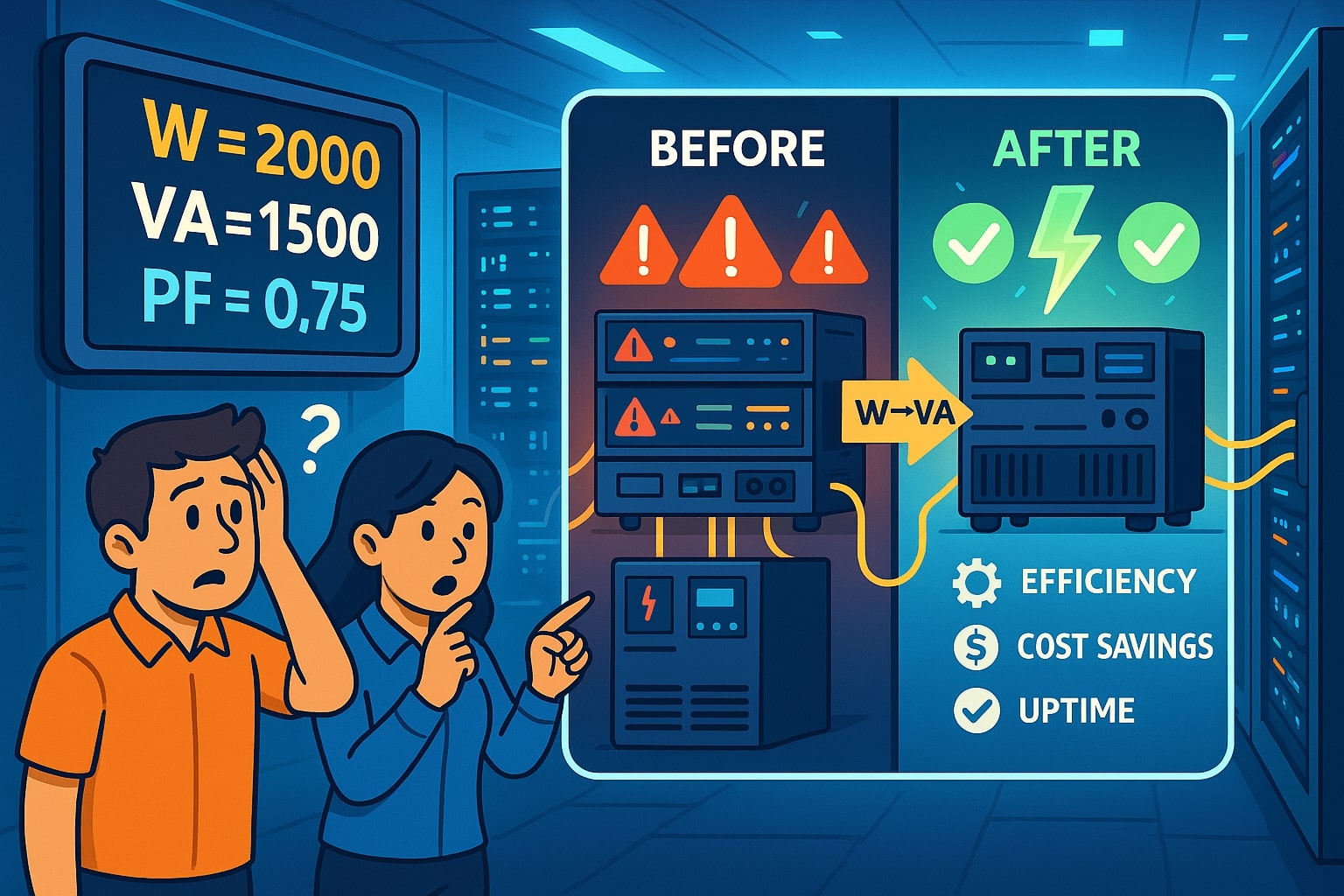
In the early 2010s, a major European telecom company expanded its data centers. The engineers calculated server needs in watts, assuming a simple one-to-one match with VA ratings. However, their UPS systems were labeled in volt amperes, and with a PF of only 0.75, the actual usable load was far lower than expected.
The result? The company invested in UPS units they thought could handle 2000 W, but in practice, each could only support 1500 W. This mismatch caused costly replacements and downtime.
The incident became a wake-up call for IT managers: watt to volt ampere conversion is not just technical math—it directly affects budgets, efficiency, and uptime. By paying attention to PF, companies can save millions and ensure their infrastructure runs smoothly.
From Math to Reliable Systems: The Value of W to VA
Accurate conversion from watt to volt ampere is vital in both households and industries. Alongside W to VA, our Power Converter covers the full range of energy units, from milliwatts to megawatts. Pair it with the all-in-one Conversion Tools for complete accuracy.
The conversion from watt to volt ampere (W to VA) ensures your systems are not only efficient but also safe. It bridges the gap between the real power you use and the apparent power your equipment must handle. With Jetcalculator, you can master this conversion and make smarter energy decisions—whether for a home office or a global data center.

