gigawatt to megawatt – How to convert GW to MW
The gigawatt (GW) is used to describe massive energy production, such as national power stations and large renewable plants. The megawatt (MW), meanwhile, is more common in projects like wind farms, data centers, and municipal energy systems. Converting gigawatt to megawatt helps us break down large-scale energy into numbers that engineers and the public can relate to.
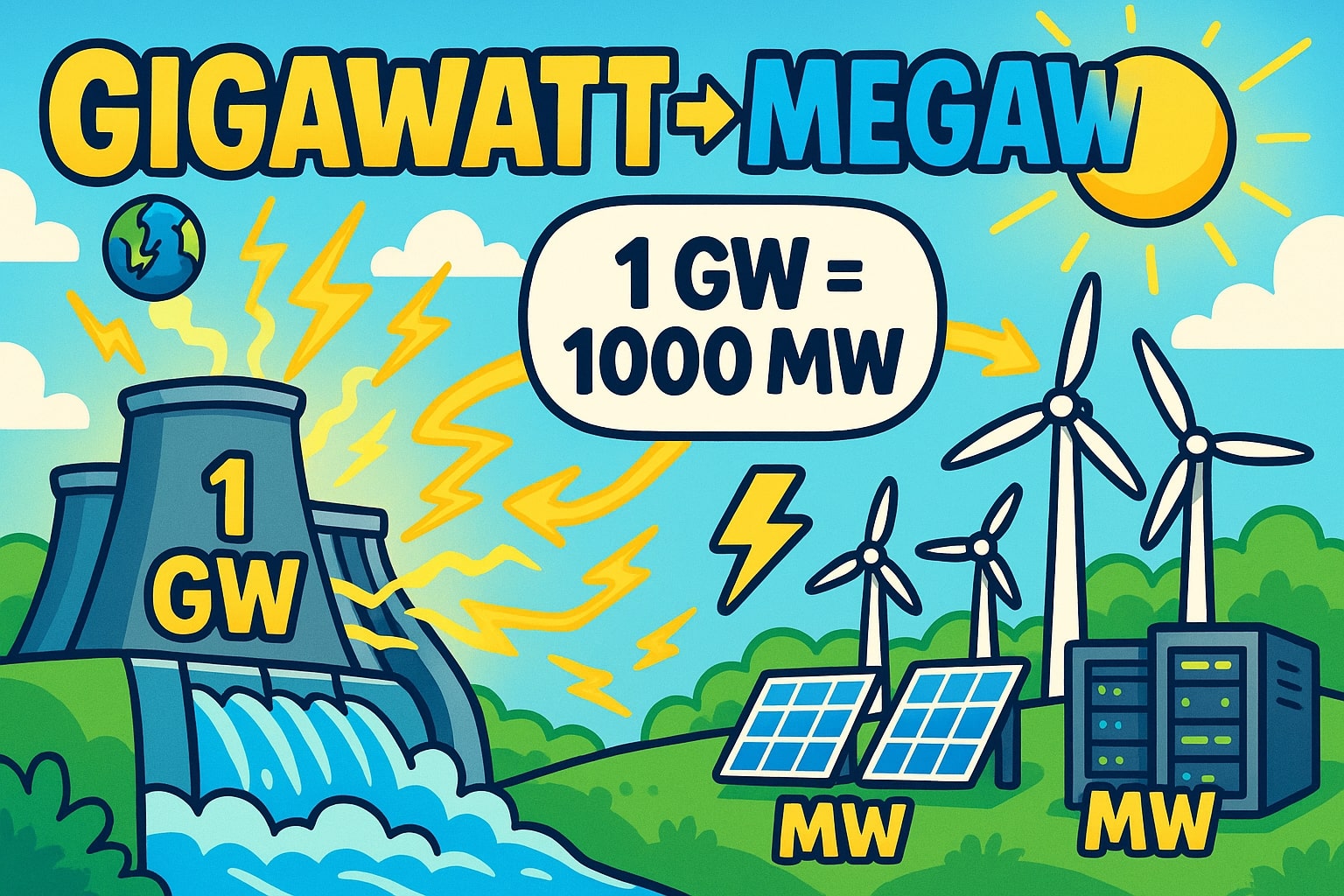
What is a gigawatt (GW)?
A gigawatt equals one billion watts (1,000,000,000 W). It is typically used for very large-scale energy capacity, such as nuclear plants or entire city grids.
What is a megawatt (MW)?
A megawatt equals one million watts (1,000,000 W). It is often used for wind turbines, solar parks, and industrial facilities. For instance, a single large wind turbine might produce 2–3 MW.
How to convert gigawatt to megawatt
Megawatt (MW) = Gigawatt (GW) × 1000
Example:
Megawatt = 3 GW × 1000 = 3000 MW
For quick conversions, you can use the Conversion Tools. Other calculators like the Speed Converter are also available for related calculations.
Do you know?
-
About gigawatt: China’s Three Gorges Dam has a capacity of over 22.5 GW — that’s 22,500 MW, making it the largest power station in the world.
-
About megawatt: A single Google data center can consume more than 100 MW of power, enough to supply electricity to about 80,000 homes.
The Rise of Wind Power
In recent decades, wind power has gone from experimental to mainstream. While one turbine may produce only 2–3 MW, large offshore wind farms can collectively reach gigawatt-scale capacity. For example, the Hornsea Project in the U.K. aims to generate over 2 GW, which equals 2000 MW.
By converting GW to MW, engineers and policymakers can compare entire national energy goals with the contributions of smaller-scale renewable projects. It’s the bridge that shows how thousands of turbines add up to make a measurable dent in a country’s energy supply.

Scaling Energy for the Future
The formula is straightforward: multiply gigawatts by 1000. Yet converting gigawatt to megawatt helps us move from the scale of nations to the scale of projects. From the massive turbines of offshore farms to the servers powering the digital world, this conversion keeps the language of energy clear and practical.

